

A very thin insulating oxide layer covers the channel region it is commonly referred to as a gate oxide. The bulk material between the source and drain in a MOSFET is called the channel. This situation is reversed in a PMOS device, as shown in Figure 1(b). An NMOS device is built on a p-doped silicon substrate that has had regions of n-type material which are created using ion implantation, as shown in Figure 1(a).These n-type regions are called the source and the drain. The majority of carriers in NMOS devices are electrons while those in PMOS devices are holes.
MOSFETs can be built as either NMOS or PMOS transistors, depending on the polarities of the bulk, source and drain regions as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 shows the elements of a typical MOSFET where the transistor is built into the surface of a silicon bulk substrate. Since MOSFETs are the most widely used FET, we will use these devices to describe the components and operation of this class of transistor. FETs differ from BJTs in the way that current flow through the device is controlled the primary current flow through an FET is controlled by a small voltage applied to one of the terminals rather than by a control current flow through any part of the device. Indeed, MOSFET devices constitute the ubiquitous “bit” switch that is set to 0 (“Off” state) or 1 (“On” state) in microelectronic logic devices (i.e., computers).
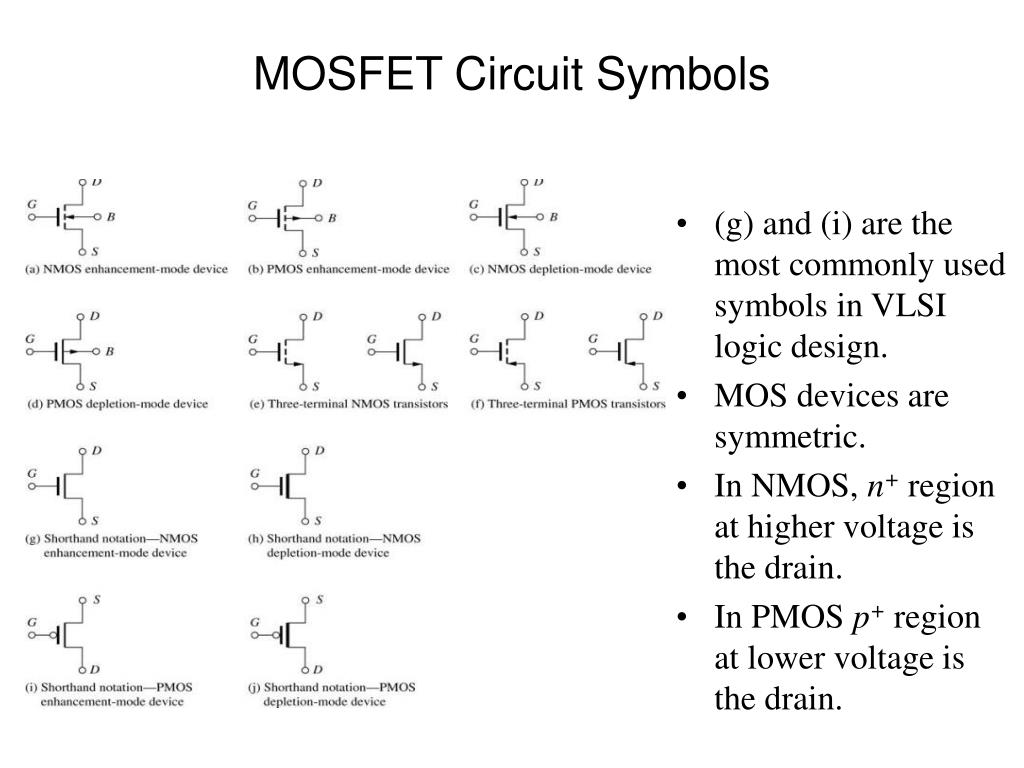
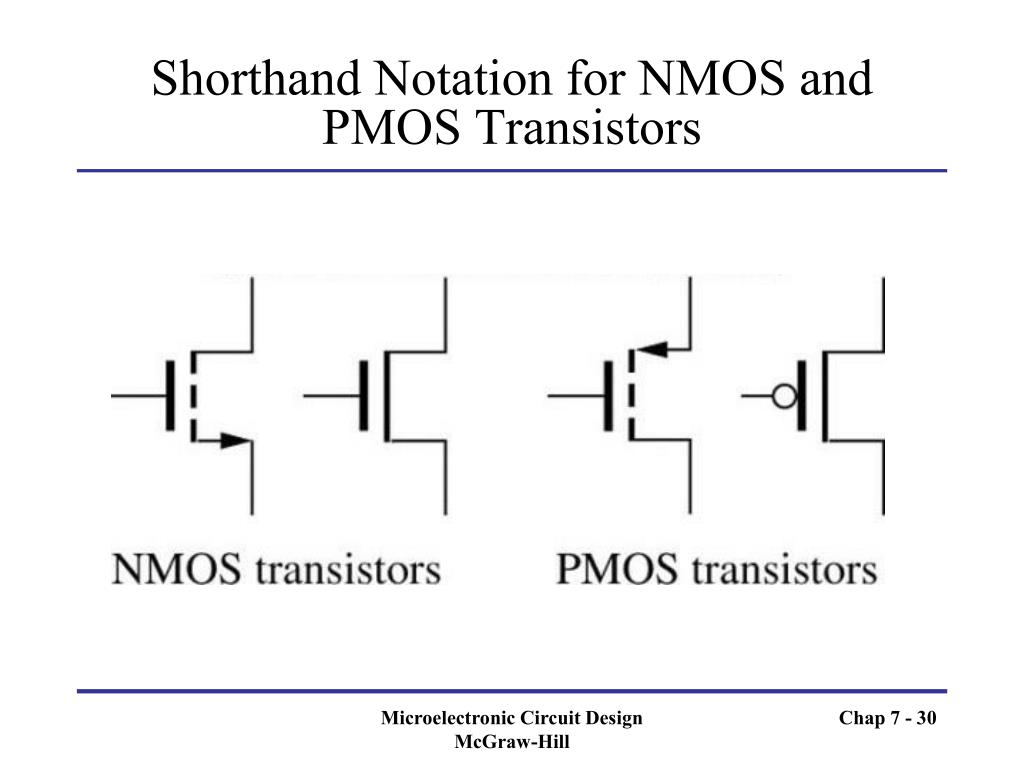
FETs can replace BJTs in most electronic circuits and have advantages for use in microelectronics since they consume and dissipate less power and they can be made much smaller than equivalent BJTs. MOSFETs are planar surface devices that are the most commonly used variant of Field Effect Transistors (FETs) the reader may also encounter Junction Gate Field Effect Transistors (JFETs) and Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistors (IGFETs). These letters are not normally included in circuit diagrams, but they are included here for clarity and explanation.Another very common form of transistor is the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET). Note: The circuit symbols for FETs are marked with D, G and S for drain, gate and source. Obviously dual gate FETs have two gates and both need to be incorporated into the circuit symbol. Insulated gate FETs, including MOSFETs have circuit symbols that indicate the insulation on the gate. Junction FETs or JFETs were the first type of FET and these have a distinctive symbol showing the diode junction. Each type of FET has its own circuit symbol, so it helps to understand the different types of FET and their circuit symbols to enable the circuits to be read accurately.

Ĭircuit symbols overview Resistors Capacitors Inductors, coils, chokes & transformers Diodes Bipolar transistors Field effect transistors Wires, switches & connectors Analogue & functional circuit blocks Logicįield effect transistors, FETs come in a large variety of different types. FET Field Effect Transistor Circuit Symbols Circuit symbols for the variety of forms of field effect transistor, FET: n-channel, p-channel, enhancement, depletion, JFET, MOSFET, dual gate FET.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
